Documentation for Class Dictioinary in 1st Use Case
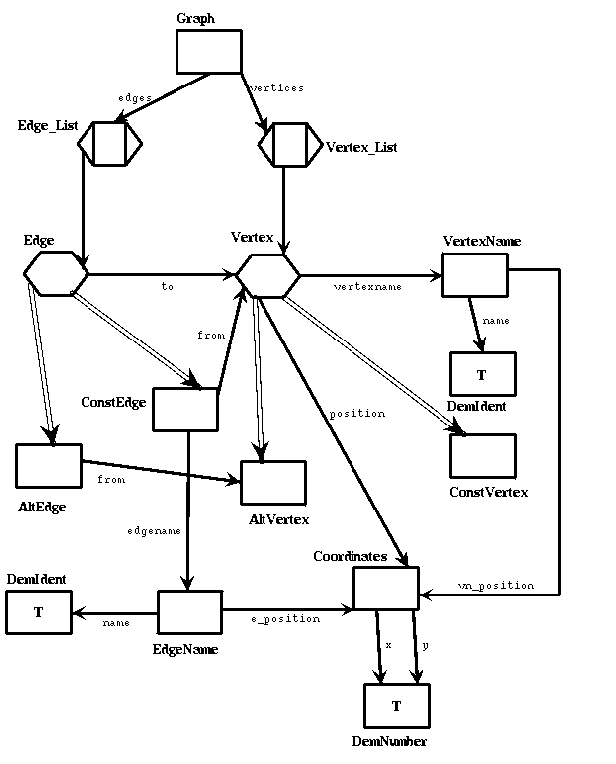
I. Textual Class Dictionary with Grammars.
II. Design Patterns Used in 1st Use Case
Adapter -- Convert the interface of a class into anther
interface clients expect, lets classes work together
that couldn't otherwise because of incompatible
interfaces.
Example: Edge: AltEdge | ConstEdge
*common* <to> Vertex.
// ConstEdge is the subclass of Edge
ConstEdge = <edgename> EdgeName
// Adapt the Vertex interface to Edge's.
<from> Vertex.
Facade -- Provide a unified interface to aa set of interfaces
in a subsystem, defines a higher level interface that
makes the subsystem easier to use.
Example: // 5 different subsystems
(1)Graph = <edges> Edge_List
<vertices> Vertex_List.
(2)ConstEdge = <from> Vertex
<edgename> EdgeName.
(3)EdgeName = <name> DemIdent
<e_position> Coordinates.
(4)Coordinates = <x> DemNumber
<y> DemNumber.
(5)VertexName = <name> DemIdent
<vn_position> Coordinates.
Factory Method -- Define an interface for creating an object,
but letting subclasses decide which class to
instantiate.
Example: Edge: AltEdge | ConstEdge
*common* <to> Vertex.
Vertex: AltVertex | ConstVertex
*common* <vertexname> VertexName
<position> Coordinates.
// ConstEdge is the subclass of Edge
ConstEdge = <edgename> EdgeName
// it decide which Vertex class it instantiates
<from> Vertex.
Interpreter -- Given a language, define a represention for
its grammar along with an interpreter that uses the
representation to interpret sentences in the language.
Example: the cd.cd provided by pp group
Iterator -- Provide a way to access the elements of an
aggregate object sequentially without exposing its
underlying representation.
Example:
//list of edges
Edge_List ~ Edge { Edge }.
//list of vertices
Vertex_List ~ Vertex { Vertex }.



























